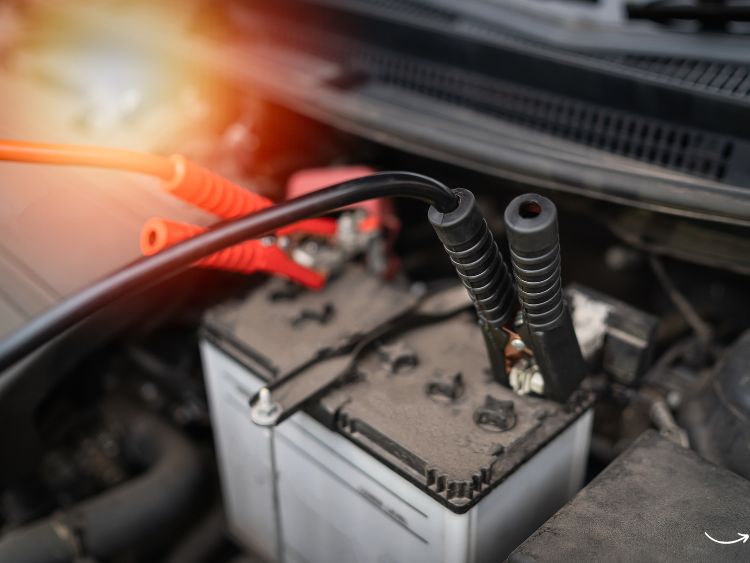
In the world of car maintenance, there’s one unsung hero that often goes unnoticed until it’s too late: the automotive battery. It’s the powerhouse of every vehicle, delivering the necessary energy to start the engine, power the lights, and keep all electrical systems running smoothly. Without a reliable automotive battery, your car won’t go anywhere. This article covers everything you need to know about automotive batteries—from types and features to maintenance tips and FAQs—helping you keep your ride fully powered.
What Is an Automotive Battery?
An automotive battery is a rechargeable device that supplies electrical energy to a car’s starter motor, lighting, and ignition systems. It acts as the heart of a car’s electrical framework, storing energy and releasing it to kickstart the engine or support other accessories.
Modern vehicles rely on sophisticated electrical systems, and the battery plays a vital role in maintaining these systems. Whether you’re driving a traditional gasoline car or a hybrid, the right automotive battery ensures smooth functionality.
Types of Automotive Batteries
When it comes to choosing an automotive battery, you’ll find several options on the market. Each type offers unique advantages, and the best choice often depends on your vehicle’s specific needs.
1. Lead-Acid Batteries
- Flooded (Wet Cell): These are the classic car batteries that are affordable and commonly used. However, they require regular maintenance to check and refill the water levels.
- Enhanced Flooded Battery (EFB): This is a more durable version of the traditional flooded battery, offering better cycling capabilities. It’s typically used in vehicles with start-stop technology.
2. Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
- Known for their longer lifespan and better resistance to vibration, AGM batteries are increasingly popular. They are sealed, maintenance-free, and ideal for vehicles with a lot of electrical demands.
3. Gel Cell Batteries
- Gel cell batteries use a gel-like substance instead of liquid, making them spill-proof and suitable for deep-cycle applications. However, they can be more expensive and are not ideal for extreme temperatures.
4. Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Typically found in electric and hybrid vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are lightweight, long-lasting, and can handle more charge cycles. However, they are also the most expensive option.
Signs You Need a New Automotive Battery
No battery lasts forever, and knowing when to replace yours is key to avoiding unexpected breakdowns. Here are some telltale signs that it’s time to invest in a new automotive battery:
- Slow Engine Crank: If your engine struggles to start, your battery may be losing power.
- Dim Lights: Dimming headlights or dashboard lights could mean the battery is weak.
- Clicking Sound: Hearing a clicking sound when you turn the key? That’s often a sign of a dying battery.
- Frequent Jump Starts: If you constantly have to jump-start your car, it’s likely time for a new battery.
- Corrosion: Look for white, ashy residue around the battery terminals; corrosion is a strong sign of battery deterioration.
How to Choose the Right Automotive Battery
Selecting the right battery can seem overwhelming, but focusing on a few essential factors can simplify the decision.
- Size: Check your vehicle’s manual for the correct battery size. Automotive batteries come in different sizes, usually designated by a group number.
- Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): This rating measures the battery’s ability to start the engine in cold temperatures. If you live in a colder climate, a higher CCA rating is essential.
- Reserve Capacity (RC): RC is the battery’s ability to keep the car running on battery power alone. A higher RC rating provides a longer backup in case of alternator failure.
- Maintenance Needs: Some batteries require regular maintenance, while others are maintenance-free. Choose one that fits your lifestyle and willingness to maintain it.
- Warranty: A longer warranty period often indicates higher quality, giving you peace of mind about the battery’s durability.
Tips for Maintaining Your Automotive Battery
Once you’ve invested in a good automotive battery, you’ll want to make it last as long as possible. Here are some tips for prolonging your battery’s lifespan and ensuring reliable performance.
- Regularly Inspect Terminals: Clean any corrosion from the terminals and ensure they’re tightly connected.
- Avoid Short Trips: Short trips don’t give the battery enough time to recharge. Try to drive longer distances occasionally to recharge it fully.
- Limit Electrical Use When Idling: Avoid using lights, the radio, or other accessories when the engine is off to prevent unnecessary battery drain.
- Keep It Charged: If you don’t drive often, consider using a trickle charger to keep the battery charged.
FAQs About Automotive Batteries
Q: How long does an automotive battery usually last?
A: On average, automotive batteries last between 3 to 5 years. Factors like climate, driving habits, and maintenance can impact battery life.
Q: Can I replace my automotive battery myself?
A: Yes, replacing a car battery is generally straightforward. However, some modern vehicles have more complex electrical systems that may require a professional’s help.
Q: How can I tell if my battery is failing?
A: Slow cranking, dim lights, frequent need for jump starts, and visible corrosion are all signs of a failing battery.
Q: What is the best type of battery for a car with high electrical demands?
A: AGM batteries are excellent for vehicles with high electrical demands due to their longer lifespan and durability.
Q: Are there any special requirements for batteries in hybrid or electric vehicles?
A: Yes, hybrid and electric vehicles use lithium-ion or specialized high-voltage batteries, which are different from traditional automotive batteries. Replacing these often requires a trained technician.
Q: Is it safe to jump-start a car with a dead battery?
A: Yes, as long as you follow the correct procedure and use high-quality jumper cables. However, it’s a temporary fix, and you should consider getting a replacement if the battery frequently needs a jump-start.
Summary
An automotive battery may seem like a small component, but it’s crucial for the smooth operation of your car. By understanding the types of batteries, recognizing signs of failure, and maintaining your battery properly, you can ensure a more reliable ride. Whether you’re a seasoned driver or a newbie, knowing these basics helps you make informed decisions that save time and money.
When it’s time to replace your automotive battery, choose the one that best suits your driving needs and climate. Stay vigilant with maintenance, and you’ll enjoy a battery that performs well for years.
Authoritative Links
- Battery Council International: www.batterycouncil.org
- Consumer Reports on Car Batteries: www.consumerreports.org/cro/car-batteries.htm
- Department of Energy: Energy Storage Basics: www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles/fact-928-august-15